Unlocking Wealth through Private Lending: An Investor’s Guide
Last week we made The Case for Alternative Investments. Today, we’re going to zoom in on a specific type of alternative investment, private lending.
Private lending is a form of direct investment where individuals or entities lend capital to businesses or individuals. Unlike traditional loans from financial institutions, private loans are often more flexible and can be customized to meet the unique needs of the borrower.
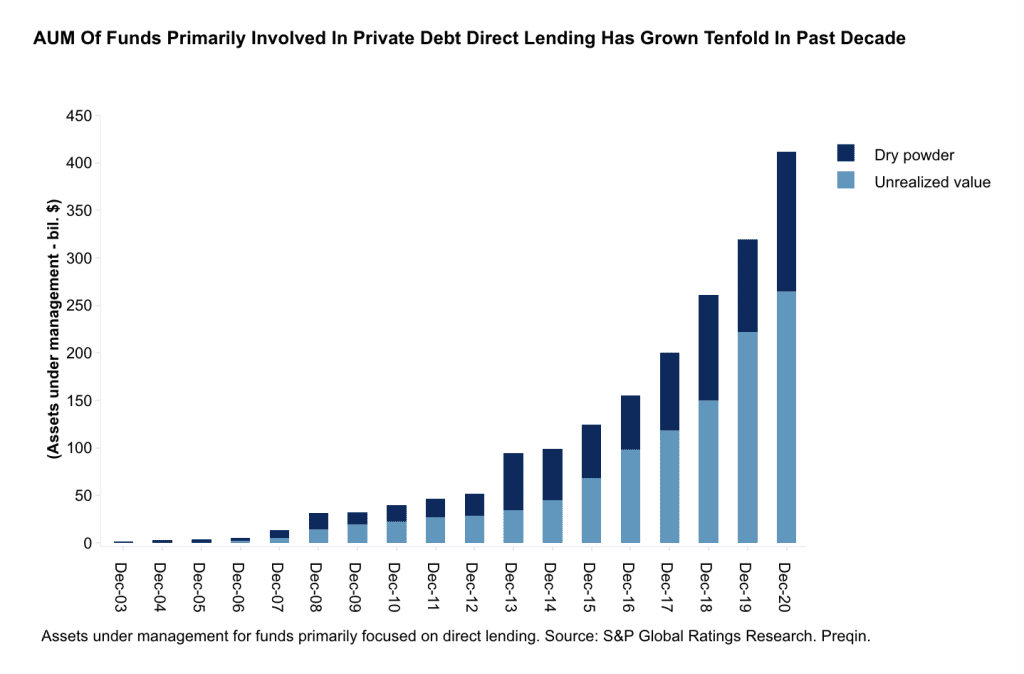
Private lending can be a powerful tool in an investor’s arsenal. It not only provides a steady stream of income through interest payments, but also allows investors to reduce exposure to market volatilities often associated with other asset classes. As the chart below shows, private debt direct lending is growing quickly.
The Basics of Private Lending:
Private lending can be categorized into several types including bridge loans, hard money loans, asset-based loans, and others. Unlike traditional lending, private lending often involves shorter loan terms, higher interest rates, and is less regulated.
Advantages of Private Lending for Wealth Building:
- Predictable Income: Through interest payments, private lending offers a predictable income stream.
- Collateral Security: Loans are often secured by assets, providing a layer of protection to the lender.
- Higher Interest Rates: Private loans often carry higher interest rates compared to traditional loans, which can lead to higher returns on investment.
- Asset Diversification: Including private lending in your investment portfolio can provide diversification, which is key to managing risk and achieving more stable returns over time.
- Customization and Flexibility: Private lending agreements can be tailored to meet the specific needs and preferences of the lender and borrower, including the loan terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules.
Risks and How to Mitigate Them:
- Credit Risk: Evaluating the creditworthiness of the borrower is crucial to ensure the borrower will not default on their obligations.
- Legal Risk: Ensuring all legal documentation is in place can mitigate risks and ensure compliance with local laws and regulations.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can affect the attractiveness and profitability of a private loan. A fixed-rate loan might become less attractive if interest rates rise, and vice versa.
- Liquidity Risk: Private loans are often less liquid than traditional loans or other types of investments. This means it may be harder to sell the loan or convert it to cash on short notice without incurring a loss.
- Collateral Risk: If a loan is secured by collateral, there’s a risk that the value of the collateral may decline, or that it may be difficult to liquidate in the event of a default.
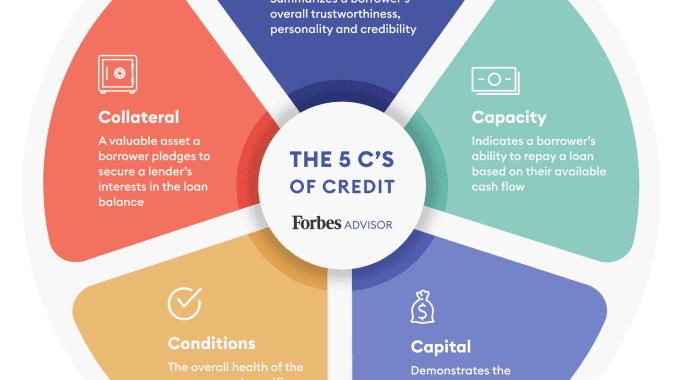
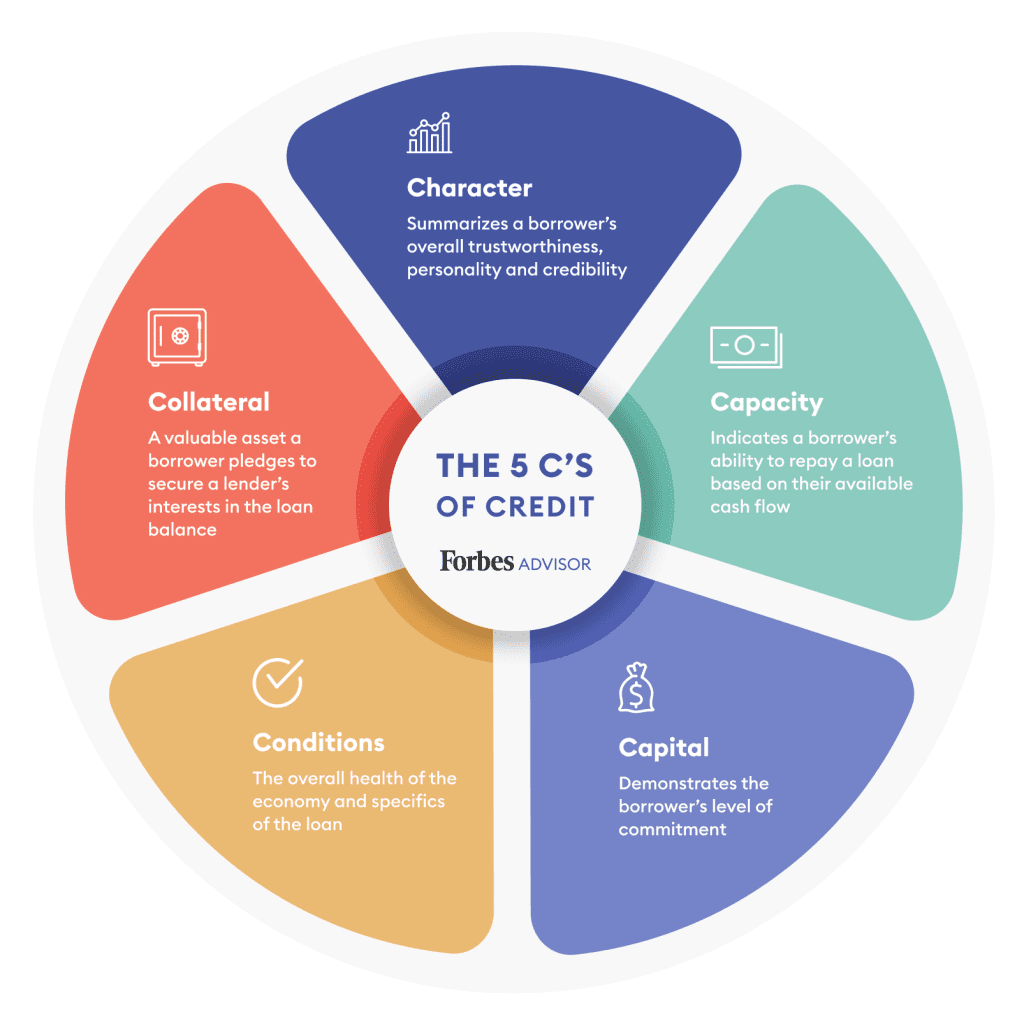
A lender often looks at the 5 C’s of Credit to determine the level of risk associated with providing the borrower with the requested funds as outlined in the chart below.
While private lending comes with its own set of risks, the potential for high returns and portfolio diversification make it a compelling choice when compared to traditional investment avenues.
Private lending emerges as a viable and potentially lucrative avenue for wealth building. With the right knowledge, due diligence, and risk mitigation strategies in place, it can significantly contribute to achieving financial empowerment.
